- Lung Care Foundation
- 011 - 4225 2328
- lung@lcf.org.in
- Home
- About Us
- Our Initiatives
- Air Pollution
- Lung Basics
- Patient Support
- Get Involved
- Media
- Contact Us
Pneumonia
- Home
What is Pneumonia?
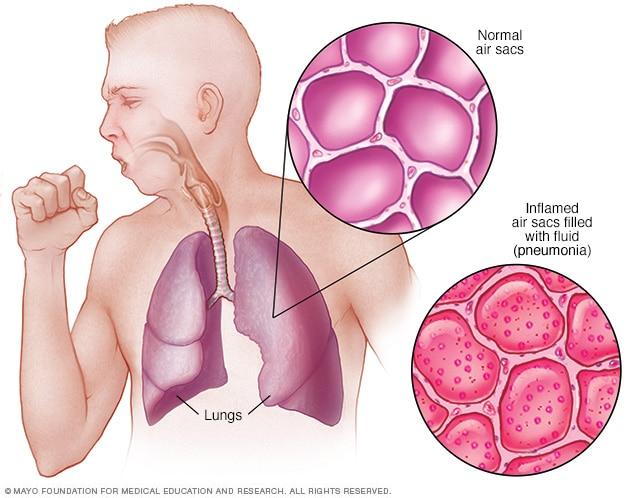
Pneumonia is an acute respiratory infection that affects the tiny air sacs in your lungs, called alveoli.
How does it affect your breathing?
When you breathe in, the germs enter your lungs and get settle in the air sacs which results in the growth of the germs and deteriorate your normal defence ability.
This results in the infection of lungs and alveoli get filled with pus and fluid which limit oxygen intake and make breathing painful and difficult.
Causes
Many different germs can cause pneumonia, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
The most common types of bacterial pneumonia are:
Bacterial Pneumonia
The most common types of bacterial pneumonia are:
- Pneumococcal pneumonia caused by a bacterium called streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Atypical pneumonia is caused by bacteria such as Legionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Chlamydophila pneumoniae.
- Other bacteria that can cause pneumonia include Staphylococcus aureus, Moraxella catarrhalis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Neisseria meningitidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae.
Viral Pneumonia
The flu virus is a common cause of viral pneumonia in adults.
Other viruses that cause pneumonia include respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus, herpes simplex virus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) virus, and more.
Fungi Pneumonia
It mostly affects those with a weak immune system.
Risk Factors
Pneumonia can affect anyone but mostly affect the high-risk group i.e. children below 2 years of age and people above 65 years.
Other risk factors include:
- Medical compromised: COPD, asthma, heart disease, HIV/AIDS, those admitted in the hospital are more prone to hospital-acquired pneumonia.
- Smoking, drinking or drug abuse.
- Exposure to toxic fumes from factories, vehicles.
Symptoms
Pneumonia symptoms vary depending on the type of pneumonia you have, your age, and any underlying lung disease.
The most common symptoms of pneumonia are:
- Cough (make cough greenish or yellow mucus or even bloody mucus)
- Fever with shaky chills
- Shortness of breath, which may only occur when you climb stairs
Additional symptoms include:
- Headache
- Chest pain when you cough or breathe
- Excessive sweating and clammy skin
- Loss of appetite and fatigue
- Confusion, especially in older people
When to Call a Doctor
If you are having difficulty breathing, cough with an increase in mucus, chest pain or if any other medical illness they should consult the doctor urgently.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask you questions regarding your symptoms and then do a physical examination.
1. Physical examination
Your doctor will listen to your lungs using a stethoscope to check for abnormal bubbling or crackling sounds that suggest pneumonia.
2. Diagnostic test
Some of the diagnosis for pulmonary fibrosis can be done easily with the help of a CT scan which reveals a honeycomb type of appearance.
- Chest X-Ray: To look for the extent of inflammation in your lungs.
- Blood test: To check white blood cell count and try to know the germ which may be in your blood as well.
- Arterial blood gases to see if enough oxygen is getting into your blood from the lungs.
- CT (or CAT) scans: CT scan of chest to get a better view of the lungs.
- Sputum tests: It is done to look for the organism (that can be detected in the mucus collected from you after a deep cough) causing your symptoms.
- Pleural fluid culture: If there is fluid in the space surrounding the lungs
- Pulse oximetry: To measure how much oxygen is moving through your bloodstream, done by simply attaching a small clip to your finger for a brief time.
Treatment
Treatment for pneumonia depends on the type of pneumonia you have and how severe it is, and if you have other chronic diseases.
Home treatment
Most people can be treated at home by following these steps:
- Drink plenty of fluids to help loosen secretions and bring up phlegm.
- Use steam to open your airways.
- Proper rest is needed. It is better to have bed rest.
-
Medicines:
Control your fever with aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen), or acetaminophen.
DO NOT give aspirin to children.
Make sure you take antibiotics as prescribed.
Emergency
Sometimes, it becomes necessary to hospitalize the person.
If your pneumonia becomes so severe that you are treated in the hospital:
- You will get fluids and antibiotics through a drip in your arm.
- You’ll also have access to oxygen if you need it, and the hospital staff can regularly check your temperature and breathing to see how you’re doing.
- You’ll usually be given two different kinds of antibiotics at the same time. You may have to take antibiotics for seven to ten days – but you won’t necessarily have to stay in hospital that long.
Recovery from Pneumonia
Better treatment is to take rest
Once you start taking antibiotics, your symptoms should begin to improve. Recovery times vary a lot from person to person and depend on your general health, age and how severe your pneumonia is.
You’ll recover gradually but eating well, exercising and doing deep breathing exercises can help in faster recovery. At first, you’ll need plenty of rest. As you begin to feel better, you can start to be a bit more active, but don’t push yourself.
A healthy young person may feel back to normal within a week of recovery from pneumonia. For middle-aged or older people, it may be weeks before they regain their usual strength and feeling of well-being.
Don’t rush recovery!
If you have taken antibiotics, your doctor will want to make sure your chest X-ray becomes normal again after you finish the whole prescription. It may take many weeks for your X-ray to clear up.
Prevention
- Wash your hands, cover your mouth is a preventive measure
- Don’t smoke, smoking aggravates the symptoms
- Proper exercise is needed but only when one is getting better. Don’t stress your body while you are serious.
- Eat a proper healthy diet which will help in fast recovery
Questions for your Doctor
- What vaccine should I take for pneumonia?
- Am I at risk of having pneumonia?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
You can consult a General Physician or your family physician.
Both viruses and bacteria can cause pneumonia.
50% are caused by viruses and are less severe than bacteria. Symptoms are milder than bacterial pneumonia like cold, dry cough, headache, fever and weakness.
Yes. The Influenza vaccine and vaccines against Pneumococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) can protect against pneumonia.
It is advisable to stop smoking since it will further irritate the already swollen and inflamed lung tissue and the tracheo-bronchial tree.
The severity of pneumonia depends on a person’s general health, age and how strong is their immune system. It is also less serious when it is caused by virus.
Pneumonia can be deadly in infants less than 2 years and elders more than 65 years. It can also be fatal in persons with weakened immune systems.
Yes it is. It can spread by inhaling the small airborne particles present in the air when someone near you has coughed or sneezed.
Most healthy people would recover in one to three weeks. Seniors and immune compromised people might take several weeks depending on their general health.
Yes, it is curable. For pneumonia caused by a virus, rest, pain killers and drinking plenty of warm fluids help. For pneumonia caused by bacteria, antibiotic treatments should be completed for full recovery.
Yes pneumonia may sometimes lead to further complications.
- Bacteraemia – Bacteria causing pneumonia may enter the blood steam and pass to other organs and rarely lead to organ failure
- Extremely difficult breathing, requiring ventilation
- Pleural effusion – Fluid may further develop within thin layers of tissue lining the lungs or pleura. This may call for a surgical treatment.
The answer is YES. Breastfeeding gives your child every essential ingredient to strengthen the immune system and thus fight away germs. However, at a tender age, care needs to be taken that your baby is kept in a clean and safe environment; even if you are breastfeeding him/her.
All Rights Reserved By LCF.ORG.IN | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions
Powered by: www.chillitrends.com
- Home
- About Us
- Our Initiatives
- Air Pollution
- Lung Basics
- Patient Support
- Get Involved
- Media
- Contact Us