- Lung Care Foundation
- 011 - 4225 2328
- lung@lcf.org.in
- Home
- About Us
- Our Initiatives
- Air Pollution
- Lung Basics
- Patient Support
- Get Involved
- Media
- Contact Us
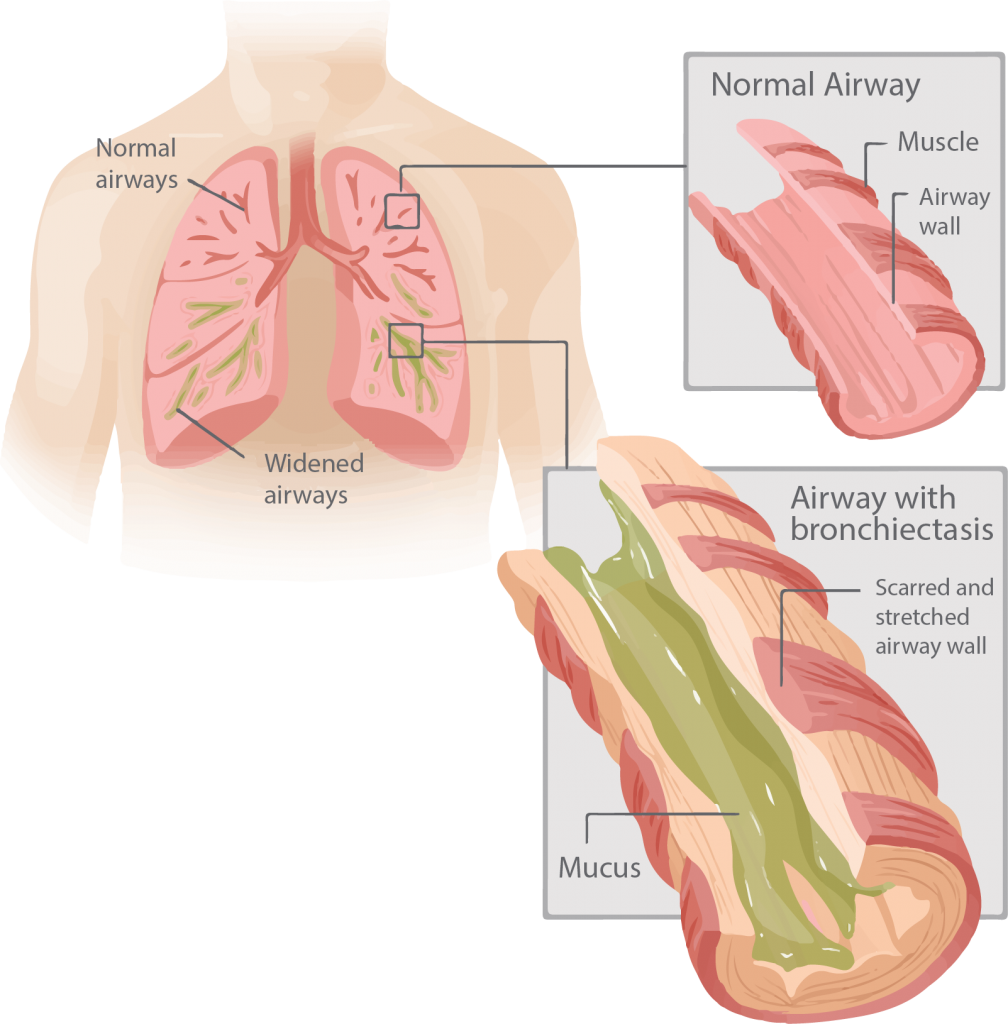
What is Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a common lung disease characterized by a chronic infection in small airways that results in some parts of the lung becomes damaged, scarred, and dilated, allowing infected mucus to build up in pockets.
Bronchiectasis results due to injury to the walls of your airways which prevent the clearing of mucus, dust, or germs leading in a collection of bacteria to grow and causing serious lung infections and inability to move air in and out.
Causes
Bronchiectasis is caused by chronic infection of the airways. The persistent airway infection and the immune response results in chronic inflammation and results in the symptoms of bronchiectasis.
Conditions associated with bronchiectasis include:
- Any past infection of the lung such as pneumonia, tuberculosis or whooping cough.
- Asthma, COPD
- Blockage in the path of your airways for example, a piece of food stuck in the airway.
- Cystic fibrosis
- Diseases that affect the tiny hair (cilia) inside the airways for example, primary ciliary dyskinesia, Kartagener’s syndrome.
- Inflammatory bowel disease also called ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
- Immune system deficiencies such as HIV/AIDS
- Arthritis disorders
- Severe allergic response to fungus or moulds such as aspergillus.
Symptoms
- Feeling short of breath
- Chest pain
- Wheezing
- Coughing up blood
- Fever
- Weekness
- Weight loss without trying
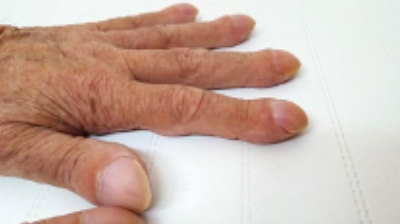
- Clubbing- thickening of finger and toenails
When to Call a Doctor
In case one experiences these symptoms then they should immediately refer to the physician or pulmonologist.
- Rapid Breathing
- Increase in temperature (100.4oF or above)
-
Cyanosis- bluish coloration of skin and lips
-
Severe chest pain
Diagnosis
- Chest X-ray – shows if there is any abnormal lung and thickened, irregular airway walls.
- Computerized tomography (CT) scans– the most common test for diagnosing bronchiectasis. A CT scan uses a special X-ray machine which shows a precise look of your lungs
- Sputum test- to check for bacteria or fungi
- Blood tests- to look for any infection or anaemia
- Lung function tests- it is done with the help of spirometer which measures your lung capacity by looking at:
- how much air you take in and out
- how well your lungs get oxygen to your blood
Treatment
Antibiotics
If you get a chest infection or have a flare-up, you’ll take a course of antibiotics, often for 14 days.
Chest physical therapy (CPT)
Clearing sputum from your lungs is very important and can reduce the number of infections you have and reduce your cough.
CPT is a way of loosening the mucus in your chest.
People usually do CPT while sitting or lying with their heads down (postural drainage).
The therapy helps loosen the mucus, and laying with your head down helps the mucus drain away from your lungs. After you’ve loosened the mucus, it’s easier to cough it up.
People with bronchiectasis often do CPT and cough up mucus three or four times a day.
There are different ways of doing chest physical therapy:
- Some people use their fist to pound on their chest
- Other people use a device, for example, an electric chest clapper, an inflated vest, a “flutter” machine or a positive expiratory pressure mask

There are also breathing exercises that help loosen mucus. Do consult your physiotherapist for the exercises.
If your sputum is sticky, and hard to cough up, your health care professional may suggest:
- A mucolytic drug to break up the sputum and make it easier to clear from your lungs.
- A nebulizer to breathe in a salt solution called saline. This may help if you have frequent infections and find it difficult to clear sputum from your lungs by physiotherapy. The saltwater helps break up the sputum and make it easier to cough up.
- Surgery- It is recommended only if none of the treatment has helped and it is affecting a single section of your lung.
Prevention
People with bronchiectasis can get flare-ups, that is, the time when their symptoms are worse. If you have bronchiectasis, stay as healthy as possible by:
- Avoiding smoking or second-hand smoke, polluted air, cooking fumes
- Eating a balanced diet and keep yourself hydrated
- Getting a flu vaccine every year
- Making sure you’ve gotten shots against measles, rubella, and pertussis(whooping cough)
- Washing your hands
- Getting help right away if you are having a flare-up
Questions for Your Doctor
- Is bronchiectasis a genetic disorder?
- I don’t smoke then why did I get it?
- What are the signs and symptoms of a flare-up?
- What can I do to prevent flare-up?
- How often should I show it to the doctor and do my mucus test?
- What if the prescribed medicines don't work out, still should I continue taking it?
- Can exercise help me out?
- What are the dietary recommendations I should take?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
If you suffer from recurrent respiratory infections or have noticed other symptoms of bronchiectasis it would be best to consult your general physician. The symptoms can easily be mistaken and confused with other conditions that affect the lungs making an accurate diagnosis all the more important. Your doctor will be able to make a diagnosis and will recommend the necessary tests to confirm his diagnosis. If necessary, he will then refer you to a specialist.
Bronchiectasis itself is not contagious as the condition results from damaged lungs or, to be more precise, the airways of the lungs. Respiratory infections like tuberculosis and whooping cough however, which can cause bronchiectasis, are contagious and anyone with a weakened immune system should exercise caution.
All Rights Reserved By LCF.ORG.IN | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions
Powered by: www.chillitrends.com
- Home
- About Us
- Our Initiatives
- Air Pollution
- Lung Basics
- Patient Support
- Get Involved
- Media
- Contact Us